Point Set Registration
Posted:
This is the project during my research visiting at Andread Nuechter’s group. The goal is to build efficient feature for very large point cloud matching, e.g., the city data, which is a challenge due to the large size of data and the weak capability of recent descriptor in such a dataset.
To achieve the goal, it consists of two subprojects.
A new formulating of registration problem
In this work, we propose to directly find the one- step solution for the point set registration problem without correspondences. Inspired by the Kernel Correlation method, we consider the full connected objective function between two point sets, thus avoiding the computation of correspondences. By utilizing least square minimization the transformed objective function is directly solved with existing well-known closed-form solutions, e.g., singular value decomposition, that is usually used for given correspondences. However, using equal weights of costs for each connection will degenerate the solution due to the large influence of distant pairs. Thus, we additionally set a scale on each term to avoid the high cost on non-important pairs. As in feature-based registration methods, the similarity between descriptors of points determines the scaling weight. Given the weights we yield a one step solution. As the runtime is in O(n2), we also propose a variant with keypoints that strongly reduce the cost. The experiments show, that our proposed method gives a one-step solution without an initial guess. Our method exhibits competitive outliers robustness, accuracy compared with various methods. And it is more stable to large rotation. In addition, though feature based algorithms are more sensitive to noise, Our method still provide better result compared with the feature match initialized ICP.
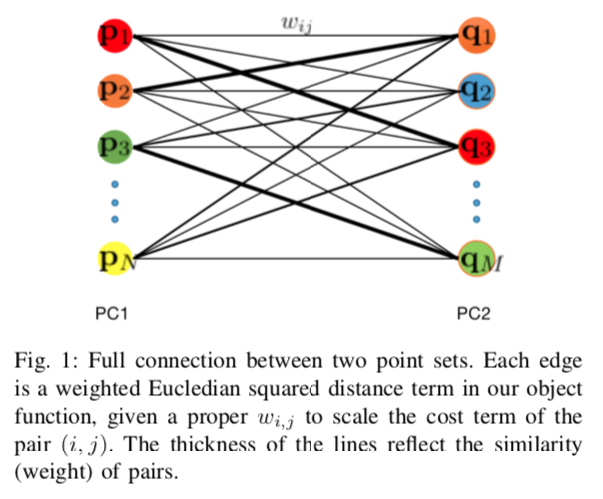
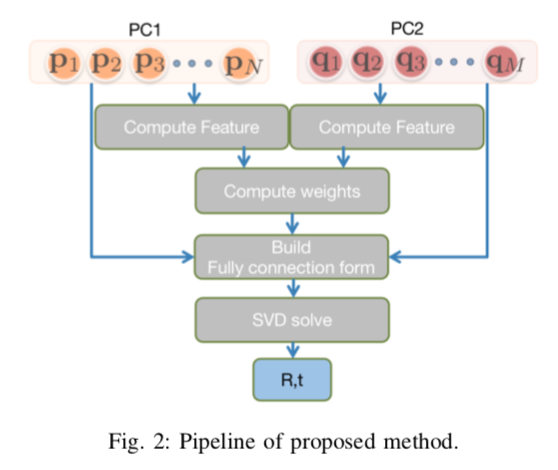
- Yuan, Y., Borrmann, D., Nüchter, A., & Schwertfeger, S. (2020). Non-iterative One-step Solution for Point Set Registration Problem on Pose Estimation without Correspondence. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.00457.
Deep feature by supervising on the one-step solved transformation
In this work, we propose to learn local descriptors for point clouds in a self-supervised manner. In each iteration of the training, the input of the network is merely one unlabeled point cloud. On top of our previous work, that directly solves the transformation between two point sets in one step without correspondences, the proposed method is able to train from one point cloud, by supervising its self-rotation, that we randomly generate. The whole training requires no manual annotation. In several experiments we evaluate the performance of our method on various datasets and compare to other state of the art algorithms. The results show, that our self-supervised learned descriptor achieves equivalent or even better performance than the supervised learned model, while being easier to train and not requiring labeled data.
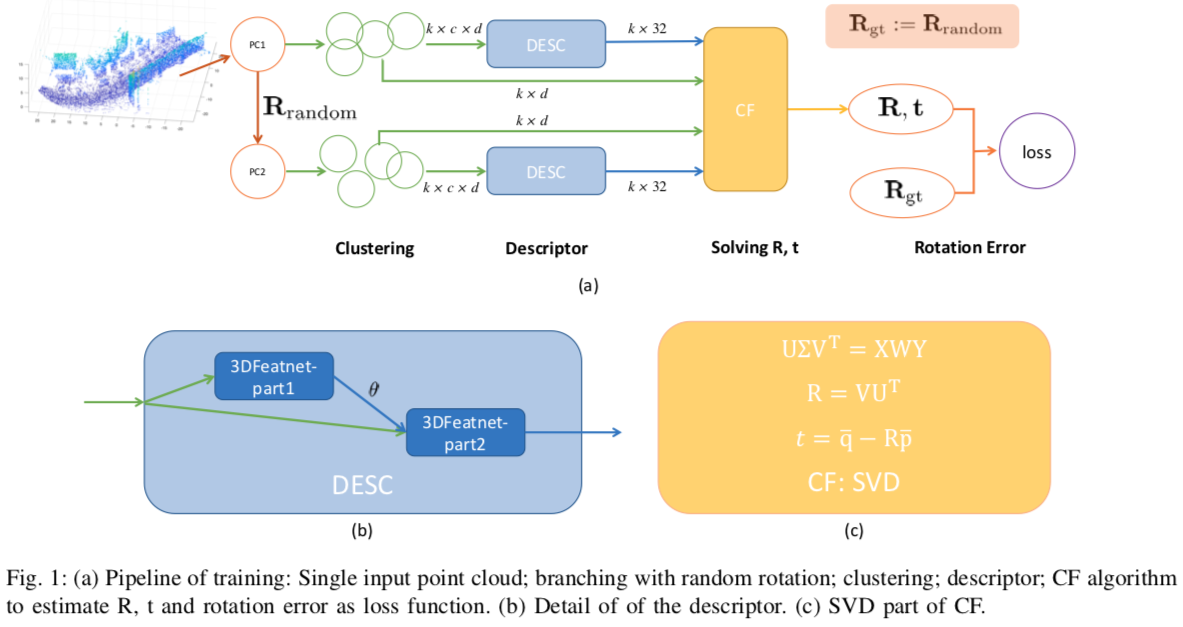
- Yuan, Y., Hou, J., Nüchter, A., & Schwertfeger, S. (2020). Self-supervised Point Set Local Descriptors for Point Cloud Registration. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2003.05199.
